Cybersecurity: The Evolution of Cybersecurity
Introduction to Cybersecurity
While the term "cybersecurity" itself emerged in the late 1980s, the roots of this field can be traced back to the dawn of information sharing. Early computer systems, though expensive and siloed, required measures to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard valuable data. Passwords, a cornerstone of cybersecurity even today, emerged from this need for controlled access in the 1960s.
Understanding the Evolution of Cyber Threats
As technology advanced and connectivity exploded, so did the sophistication of cyber threats. The 1970s witnessed the birth of the first computer viruses, malicious code designed to replicate and spread across systems. The Morris Worm of 1988, a self-replicating worm that caused widespread internet outages, became a wake-up call, highlighting the potential devastation of cyberattacks.
The 1990s saw the rise of the Internet and the commercialization of personal computers. This era witnessed a surge in hacking activities, with attackers targeting vulnerabilities in operating systems and software. Firewalls and antivirus software emerged as crucial lines of defense in this evolving battleground.
Key Threats in Modern Cybersecurity
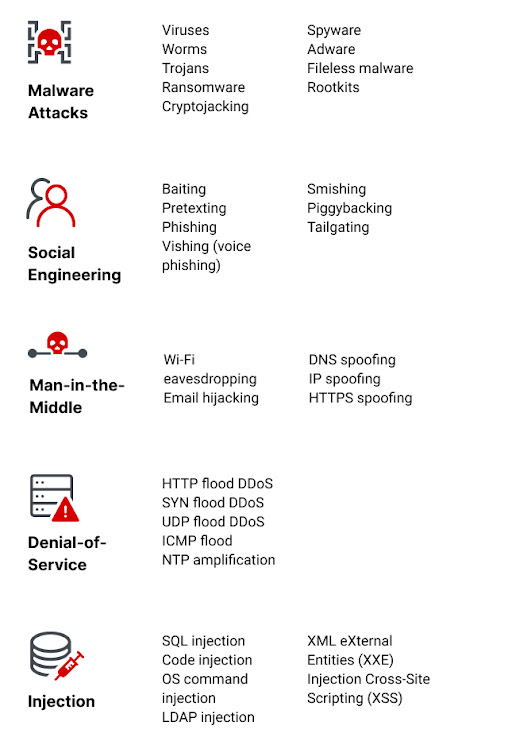
Today's cybersecurity landscape is far more complex. Hackers are no longer lone wolves; they operate in organized groups, often backed by nation-states. Their motives range from financial gain (ransomware attacks) to espionage (stealing intellectual property) and even disrupting critical infrastructure.
The rise of mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) has created a vast new attack surface. Cloud computing, while offering flexibility, also introduces new security challenges. Here are some of the key threats in modern cybersecurity:
- Ransomware: This form of malware encrypts a victim's data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Ransomware attacks have crippled businesses and government agencies alike.
- Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information or clicking malicious links. Phishing remains one of the most common cyber threats due to its effectiveness.
- Social Engineering: Attackers exploit human psychology to manipulate victims into compromising security measures. Social engineering takes many forms, including pretext calls and impersonation scams.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Hackers target software vendors or service providers to gain access to a wider network of systems.
Cybersecurity is a continuous arms race, with defenders constantly innovating to stay ahead of attackers. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security awareness training are all crucial tools in this ongoing fight. As technology continues to evolve, so too must our approach to cybersecurity. By understanding the ever-changing threat landscape and implementing robust security measures, we can work towards a more secure digital future.
Solutions and Strategies for Mitigating Cyber Threats
While the fight against cyber threats is ongoing, there are effective strategies and solutions that organizations and individuals can employ:
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cyber threats, phishing tactics, and best security practices is vital in preventing social engineering attacks and human error.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating software and operating systems with the latest security patches is crucial to address known vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, adds an extra layer of protection, making it unreadable even if intercepted by hackers.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an additional step to the login process, requiring a second verification factor beyond just a password, significantly improving security.
- Next-Generation Firewalls: These advanced firewalls can analyze network traffic to identify and block malicious activity more effectively than traditional firewalls.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems aggregate data from various security tools, providing a centralized view of potential threats and enabling faster incident response.
Historical Milestones in Cybersecurity
Several pivotal moments have shaped the evolution of cybersecurity:
- 1960s: Passwords are introduced as a basic access control mechanism for time-sharing systems.
- 1988: The Morris Worm highlights the vulnerability of interconnected systems, leading to the increased focus on cybersecurity.
- 1990s: Antivirus software becomes widespread as malware threats rise with the proliferation of personal computers.
- 2001: The September 11th attacks underscore the potential impact of cyberattacks on critical infrastructure.
- 2010s: Cloud computing adoption necessitates new security measures for data stored and accessed remotely.
- 2020s: Ransomware attacks surge, targeting businesses and government agencies with data encryption and ransom demands.
These milestones showcase the continuous adaptation of cybersecurity practices in response to emerging threats.
Emerging Challenges and Future Trends
The future of cybersecurity will be shaped by several key trends:
- The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will play a crucial role in both offensive and defensive cybersecurity strategies. Attackers will use AI to automate attacks and develop more sophisticated malware, while defenders will leverage AI for threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability analysis.
- The Expanding Attack Surface: As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, the number of potential entry points for attacks will increase dramatically. Securing these interconnected devices will be a major challenge.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to break current encryption standards. Developing post-quantum cryptography will be essential to safeguard sensitive data in the future.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: As cyberattacks become more sophisticated and damaging, governments around the world will likely implement stricter regulations to hold companies accountable for data security breaches.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Adapting to Evolving Threats and Technologies
Cybersecurity is not a static field. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, so too must our approach to protecting our digital assets. By staying informed about the latest threats, implementing robust security solutions, and fostering a culture of security awareness, we can build a more secure and resilient digital future.
Conclusion:
The ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity demands constant vigilance and collaboration. Individuals, organizations, and governments all have a role to play in securing our digital world.
By prioritizing cybersecurity awareness, investing in robust defenses, and fostering international cooperation, we can stay ahead of the curve. The future of cybersecurity lies in embracing innovation, not just in technology itself, but also in our collective strategies for defense. By working together, we can build a digital ecosystem where trust and security are not just aspirations, but realities.

Comments
Post a Comment